Introduction
Computers are everywhere — in your pocket (smartphones), cars, schools, businesses, hospitals, shops, and even home appliances. But have you ever wondered: How does a computer actually work?
What happens inside when you click something, type a message, run a game, or open a website?
This beginner-friendly guide breaks everything down in simple language so anyone — even with zero technical knowledge — can understand how computers work from the inside out.
We’ll explore computer hardware, software, memory, storage, input/output devices, processing, and the full journey of data inside a computer.
1. What Is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic machine that processes information. It takes input, performs processing, and gives output.
Simple formula:
Input ➝ Processing ➝ Output
Example
Typing on a keyboard → computer processes the keys → displays the text on screen.
2. Main Parts of a Computer
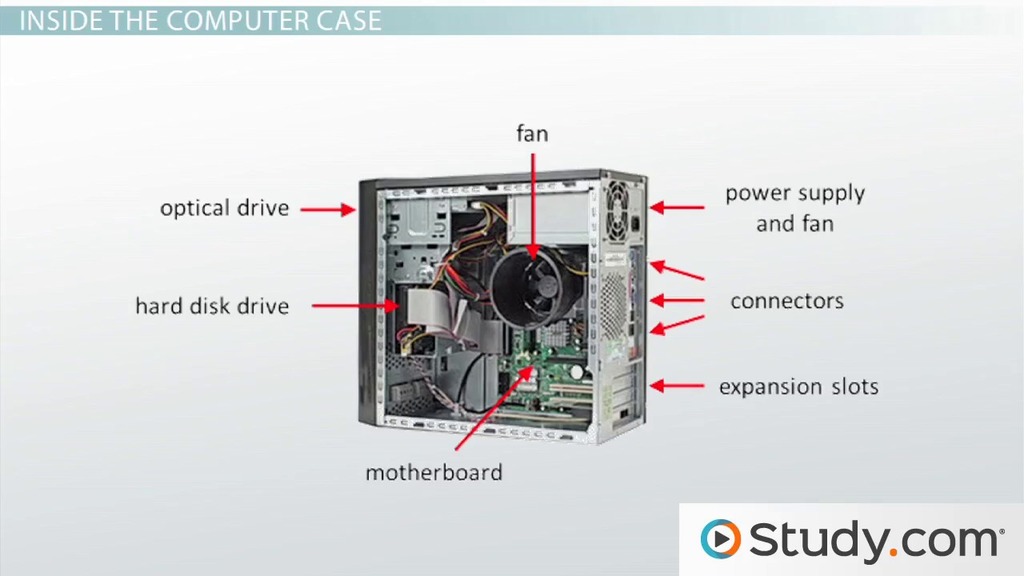

A computer has two major components:
A) Hardware
Physical parts you can touch.
Examples:
- CPU
- RAM
- Hard Drive / SSD
- Motherboard
- Keyboard / Mouse
- Monitor
B) Software
Programs that tell the hardware what to do.
Examples:
- Windows
- Android
- Web Browsers
- Games
- Apps
Both hardware and software work together to complete tasks.
3. CPU — The Brain of the Computer
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit.

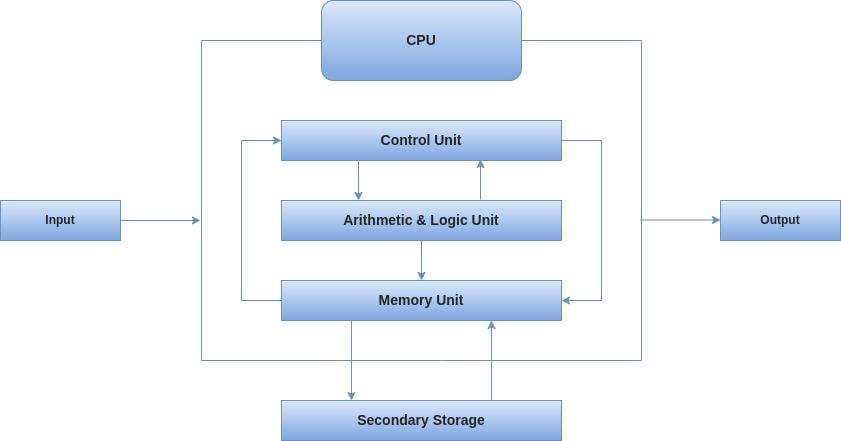
The CPU performs all calculations and processing.
Key functions
- Executes instructions
- Performs mathematical operations
- Manages data flow
- Processes programs
How CPUs work
CPUs use billions of tiny switches (transistors) that turn ON and OFF (1 and 0).
These binary values form the language computers understand.
4. RAM — Short-Term Memory
RAM = Random Access Memory
RAM temporarily stores data the CPU needs right now.
Examples of what RAM stores
- Open applications
- Browser tabs
- Running games
- System processes
Important facts
- RAM is fast
- RAM is temporary
- When the computer turns off → RAM is cleared
More RAM = better multitasking.
5. Storage — Long-Term Memory
Unlike RAM, storage keeps data even when the computer is turned off.
Types of storage
- HDD (Hard Drive): Slower, mechanical
- SSD (Solid State Drive): Faster, no moving parts
Stored items
- Photos
- Videos
- Apps
- Documents
- Operating system (Windows, Linux, macOS)
6. Motherboard — The Main Circuit Board
The motherboard connects all components.
What it does
- Allows communication between parts
- Supplies power
- Holds CPU, RAM, storage
- Provides ports (USB, HDMI, etc.)
7. Power Supply — Provides Electricity
Computers need stable electrical power to operate.
The power supply converts high-voltage electricity into safe levels for computer parts.
8. Input Devices — How You Communicate with a Computer


Examples:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Touchscreen
- Microphone
- Camera
These send information into the computer.
9. Output Devices — How Computers Communicate with You
Examples:
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speakers
- Projector
These display or deliver results.
10. How Software Works
Software is a set of instructions that tells the computer what to do.
Types of Software
A) System Software
Manages hardware.
Examples:
- Windows
- macOS
- Linux
B) Application Software
Apps people use.
Examples:
- Chrome
- Word
- Games
11. How Computers Process Information — Step-by-Step
Let’s understand the full journey of how a simple task works:
Example: Opening a Browser
- You click the Chrome icon (input)
- CPU receives instruction
- RAM loads Chrome files
- Display shows the browser window (output)
This process happens in milliseconds.
12. Binary — The Language of Computers
Computers do not understand English, Urdu, or any human language.
They understand binary:
0 = OFF
1 = ON
Everything — images, videos, text, apps — is converted into 0s and 1s.
13. Operating System (OS) — The Boss of the Computer


The OS manages everything.
Functions
- Controls memory
- Manages files
- Runs applications
- Connects hardware & software
14. GPU — The Graphics Brain
GPU = Graphics Processing Unit
Uses
- Gaming
- Video editing
- 3D modeling
- AI processing
GPUs are specialized for heavy graphic and parallel tasks.
15. How the Internet Works on a Computer
When you access a website:
- Browser sends a request
- Server receives the request
- Server sends data back
- Browser displays the website
Computers rely on:
- WiFi
- Routers
- Servers
- DNS
16. How Data Is Stored
Data is broken into bits and stored as magnetic charges (HDD) or electrical signals (SSD).
Units of data
- 1 Byte = 8 bits
- 1 KB = 1,024 bytes
- 1 GB = 1 billion bytes
17. Computer Performance — What Makes a Computer Fast?

Key factors
- CPU speed
- Number of CPU cores
- RAM size
- SSD vs HDD
- GPU power
- Software optimization
18. The Future of Computers
Trends
- Quantum computers
- AI-powered systems
- Cloud PCs
- Voice-based computing
- Augmented reality interfaces
Computers will become faster, smarter, and more integrated into daily life.
19. Common Beginner Questions
Q1: Why does a computer slow down?
- Low RAM
- Too many apps
- Full storage
- Malware
- Old hardware
Q2: What is the difference between CPU and GPU?
CPU = multitasks
GPU = handles graphics & parallel tasks
Q3: Do all computers work the same way?
Yes — phones, laptops, tablets all follow input → process → output.
Conclusion
Computers are powerful machines built from both hardware and software working together. Even though everything happens incredibly fast, the core idea remains simple: a computer takes input, processes it, and outputs results.
Understanding these basics helps beginners confidently navigate the digital world and builds a foundation for learning programming, IT, or advanced computer science.
Computers run the modern world — and now you understand how they work from the inside out.




Leave a Reply