Introduction
Robotics is becoming one of the most revolutionary technologies of the 21st century. From automated factories to smart home assistants, robots are everywhere. As of 2025, more than 3.9 million industrial robots are operating in factories worldwide, and billions of people interact with robots daily through AI assistants, delivery bots, automated checkouts, and smart appliances.
This guide explains how robotics is transforming manufacturing, business, healthcare, transportation, and everyday human life.
A perfect beginner-friendly and industry-level explanation.
1. What Are Robots? (Simple Explanation)
A robot is a programmable machine designed to perform tasks automatically.
Key characteristics
- Can sense the environment
- Can make decisions (using AI)
- Can move or manipulate objects
- Can perform repetitive or dangerous tasks
Types of robots
- Industrial robots
- Service robots
- Medical robots
- Household robots
- Autonomous vehicles
- Humanoid robots
Robots + AI = Smart automation.
2. Robotics in Manufacturing — The Biggest Transformation
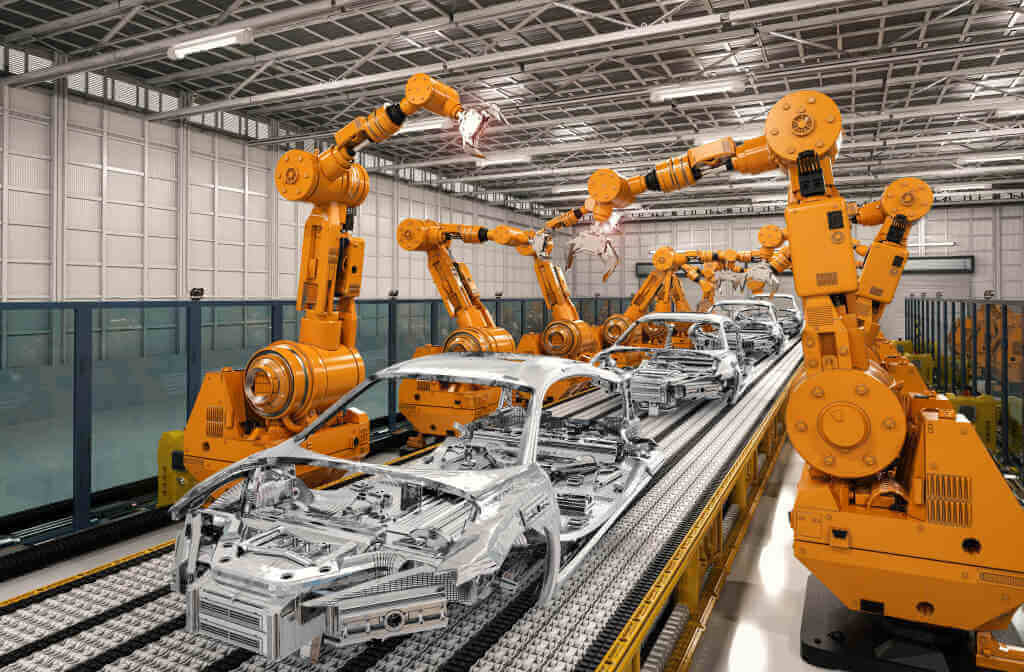

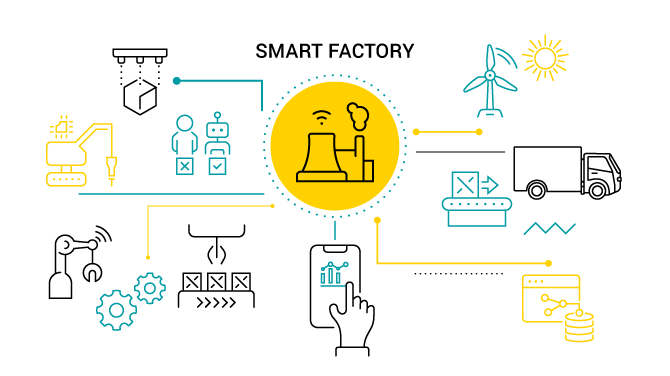

Manufacturing is the No.1 industry transformed by robotics. Factories now use robots for tasks that require speed, accuracy, strength, and 24/7 operation.
A) Assembly Line Automation
Robotic arms assemble products like cars, electronics, and appliances with extreme precision.
Benefits
- Faster production
- Zero fatigue
- Fewer errors
- Consistent quality
B) Welding & Painting Robots
Robots handle dangerous tasks like welding and painting to protect human workers from hazards.
C) Packaging & Sorting Robots
Robots identify products using sensors and cameras and sort them faster than humans.
Used in:
- Food factories
- Amazon warehouses
- Logistics centers
D) Quality Control Using AI Vision
AI-powered cameras inspect products for defects with 99% accuracy.
Detects:
- Cracks
- Misalignments
- Surface defects
- Incorrect assembly
E) Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots work with humans, not replace them.
Benefits
- Safe interaction
- Low cost
- Easy to program
- Perfect for small businesses
F) Predictive Maintenance Robots
Robots monitor machines and predict when equipment will break.
Impact
- Reduces downtime
- Saves money
- Extends machine lifespan
3. Robotics in Warehousing & Logistics
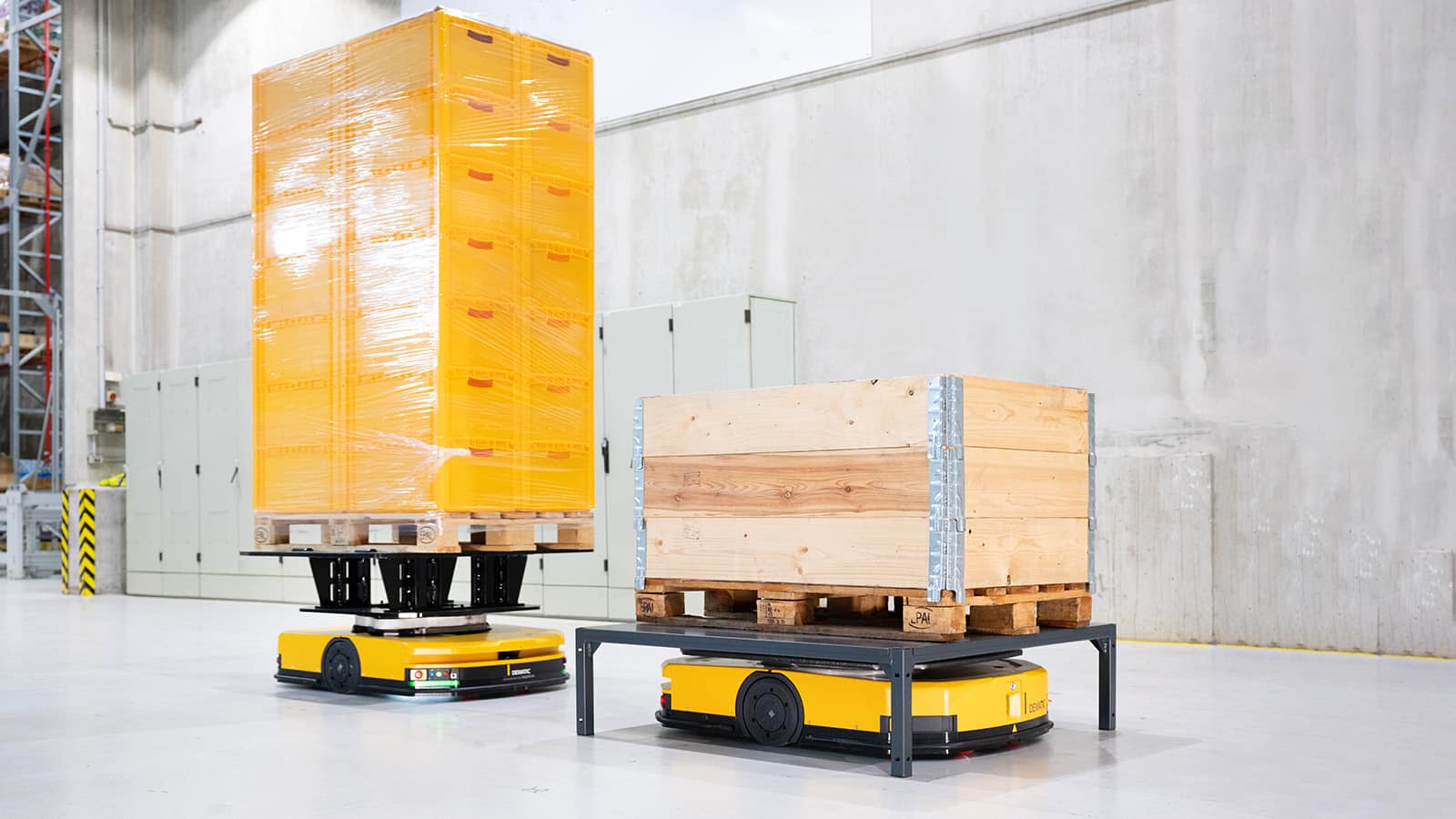


E-commerce companies are the biggest users of warehouse robots.
Common robotic systems
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
- Shelf-moving robots
- Conveyor bots
- Autonomous forklifts
Benefits
- Faster order fulfillment
- Reduced labor cost
- Safer warehouse operations
- 24/7 productivity
Amazon uses more than 750,000 robots in its fulfillment centers.
4. Robotics in Healthcare
Robots are transforming medical procedures, patient care, and hospital operations.

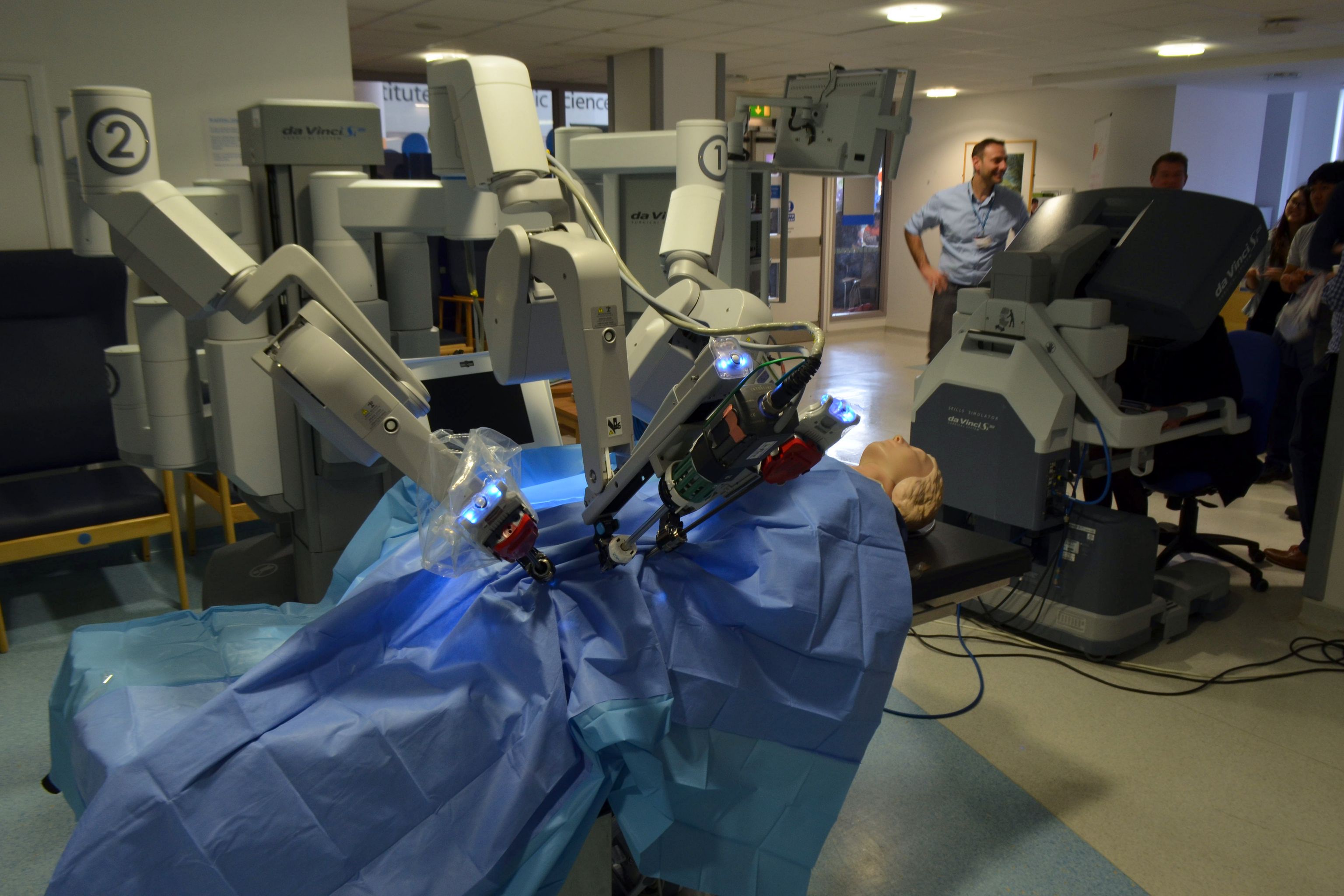
A) Surgical Robots
Robots like the Da Vinci Surgical System allow doctors to perform minimally invasive surgeries.
Benefits
- Smaller incisions
- Faster recovery
- Higher precision
B) Rehabilitation Robots
Used to help patients recover from strokes or injuries.
C) Pharmacy Automation Robots
Robots fill prescription orders quickly and accurately.
D) Hospital Service Robots
Robots deliver medicine, food trays, and even disinfect rooms using UV light.
5. Robotics in Daily Life — Everyday Use Cases
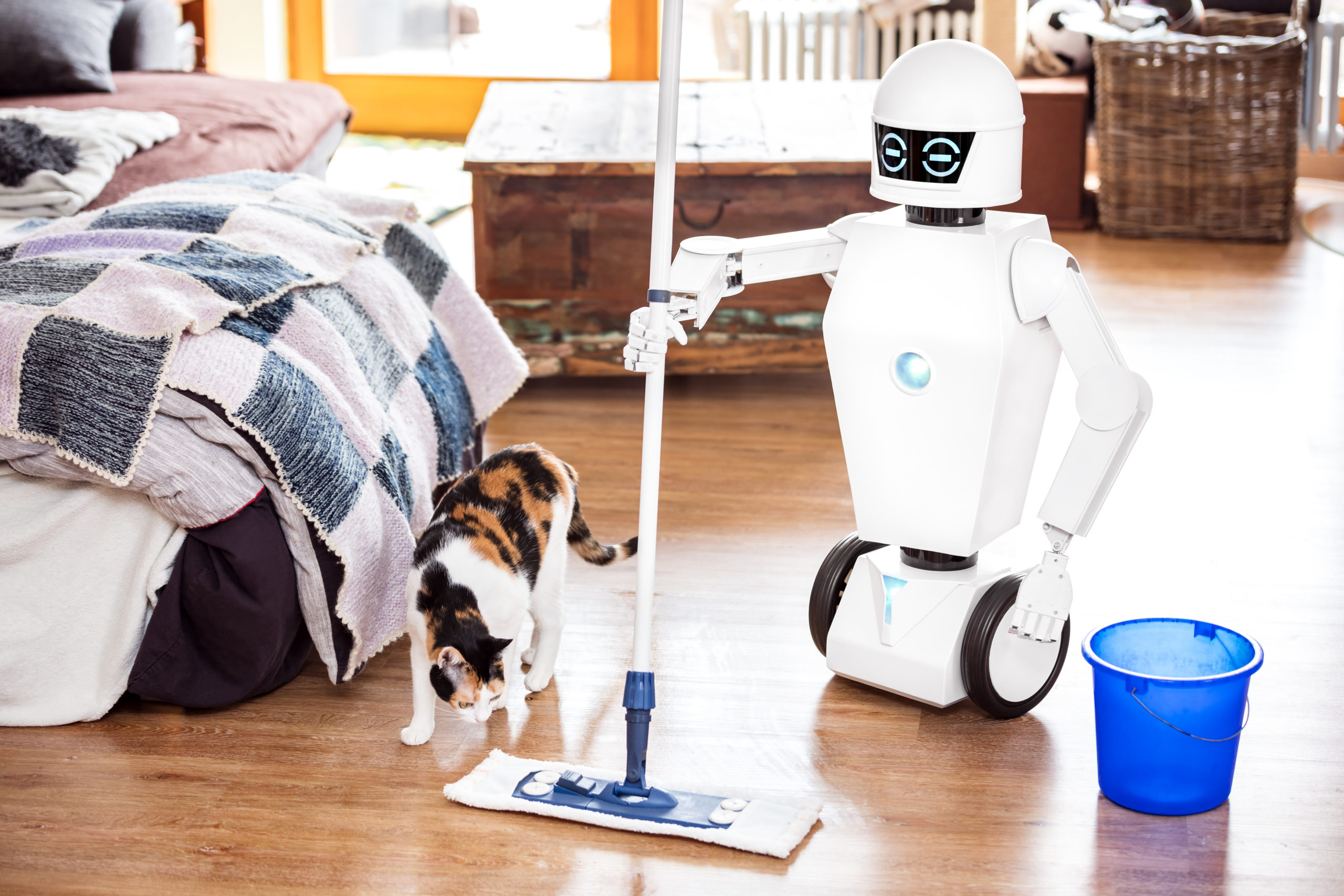


Robots are now a part of our homes and routines.
A) Smart Home Robots
- Vacuum robots (Roomba)
- Window-cleaning robots
- Lawn-mowing robots
- Pet-feeding robots
B) Voice Assistants (AI Robots)
Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri are technically robots powered by AI.
They can:
- Answer questions
- Control smart devices
- Manage schedules
- Play music
C) Personal Assistant Robots
Humanoid robots assist elderly or disabled people.
D) Cooking Robots
Kitchen robots can prepare recipes, chop vegetables, and cook meals.
6. Robotics in Transportation
Self-driving cars, trucks, and drones are transforming mobility.
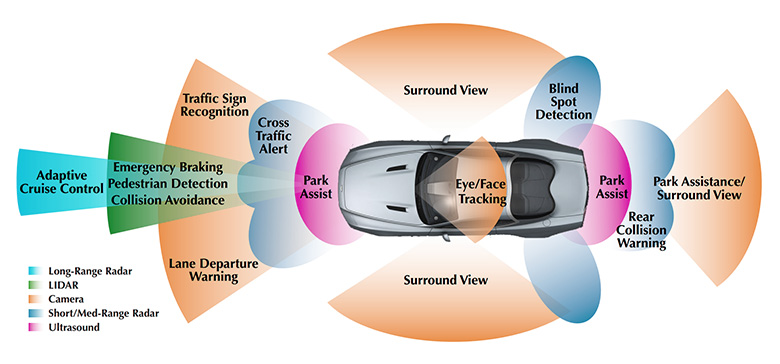


A) Autonomous Cars
Developed by Tesla, Google Waymo, and other companies.
Capabilities
- Lane detection
- Traffic prediction
- Automatic braking
- Self-parking
B) Delivery Drones
Used by Amazon, Walmart, and food delivery companies.
Benefits
- Fast delivery
- Reduced traffic
- Lower carbon emissions
C) Autonomous Trucks
Used for long-distance transportation to reduce fatigue and accidents.
7. Robotics in Education
Robots are used to teach coding, engineering, language, and STEM skills.
Examples
- AI tutors
- Robot teachers
- Educational robot kits
Robots make learning interactive and engaging.
8. The Benefits of Robotics Across Industries

A) Increased Productivity
Robots can work continuously without breaks.
B) Higher Accuracy
Robots reduce human mistakes.
C) Improved Safety
Dangerous tasks are handled by robots instead of humans.
D) Lower Costs
Automation reduces long-term operational expenses.
E) Faster Delivery of Products
Especially in e-commerce, logistics, and food delivery.
9. Challenges of Robotics
A) High Cost of Adoption
Advanced robots require large investment.
B) Job Displacement Concerns
Some traditional jobs are replaced by automation.
C) Technical Issues
Robots require maintenance and monitoring.
D) Cybersecurity Risks
Smart robots connected to the internet can be hacked.
10. The Future of Robotics (2025–2035)



Major trends
- Human-like humanoid robots
- AI-driven personal assistants
- Fully automated factories
- Robot doctors & nurses
- Space robots for Mars/Moon missions
- Emotional AI robots
Robotics is becoming smarter, safer, more affordable, and more human-friendly.
Conclusion
Robotics is reshaping manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, homes, and everyday life. From automated factories to helpful home robots, robotics technology is improving efficiency, safety, and convenience across the world.
The future will be a world where humans and robots work side by side — combining human creativity with robotic strength and precision. Businesses that adopt robotics now will lead their industries in the coming decade.
As we move into a smarter and more automated future, robotics will remain one of the most exciting and impactful technologies transforming society.




Leave a Reply