Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses, developers, and individuals store data, run applications, and manage IT systems. Instead of buying expensive servers and maintaining local hardware, companies now use the cloud—a global network of remote servers hosted on the internet.
Today, more than 94% of enterprises use cloud services, and the global cloud industry is expected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2030. The cloud is the backbone of modern digital transformation, powering everything from streaming platforms, online stores, mobile apps, artificial intelligence tools, and global businesses.
This guide will explain cloud computing in simple language, explore its types, benefits, and share real-world use cases used by top companies.
1. What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing services—such as storage, servers, databases, software, and networking—over the internet instead of your local computer.
Simple definition:
Cloud computing means using someone else’s computer (the cloud provider) to store data, run applications, and process information over the internet.
Key features
- No hardware needed
- Pay only for what you use
- Access from anywhere
- Scalable and flexible
Cloud providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Microsoft Azure
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
These companies run massive data centers globally, offering computing power to millions of businesses.
2. How Cloud Computing Works
Cloud computing is made possible by remote data centers—high-performance servers that run applications and store data.
When you upload a file, stream a movie, or run an app:
- Your device connects to the cloud.
- The cloud provider processes your request.
- The data or application is delivered back instantly.
Key components
- Front-end: User devices & applications
- Back-end: Servers, storage, data centers
- Network: Internet connecting everything
Why it matters
It removes the need for physical infrastructure and allows businesses to scale instantly.
3. Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing services are divided into three main types:

A) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This is the most basic level—renting virtual servers and storage.
Examples
- AWS EC2
- Google Compute Engine
- Azure Virtual Machines
Used for
- Hosting websites
- Running apps
- Data storage
- Testing environments
B) Platform as a Service (PaaS)
This provides tools for developers to build and deploy applications without handling servers.
Examples
- Google App Engine
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Heroku
Used for
- App development
- Automation
- Deploying websites
C) Software as a Service (SaaS)
These are complete applications hosted on the cloud.
Examples
- Gmail
- Zoom
- Shopify
- Salesforce
Used for
- Business software
- Collaboration
- Online stores
- Communication
4. Cloud Deployment Models
There are four ways clouds are deployed based on usage:
1. Public Cloud
Used by multiple companies; managed by providers like AWS or GCP.
✔ Affordable
✔ Scalable
✔ Easy to use
Best for startups and general businesses.
2. Private Cloud
Exclusive cloud for a single organization.
✔ High security
✔ Full control
✔ Ideal for banks & government
3. Hybrid Cloud
Combination of public + private clouds.
✔ Best of both worlds
✔ Highly flexible
Most enterprises use hybrid clouds today.
4. Multi-Cloud
Using multiple cloud providers at once.
✔ Avoid vendor lock-in
✔ Higher reliability
5. Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers massive advantages for all types of users.


A) Cost Savings
Cloud eliminates the need for expensive hardware.
- No buying servers
- No maintenance cost
- Pay-as-you-go billing
B) Scalability
You can increase or decrease cloud resources instantly.
Example:
E-commerce stores scale up during Black Friday traffic.
C) Speed & Performance
Cloud data centers use advanced hardware and fast networking.
- Lower latency
- Faster loading times
- More reliable apps
D) Global Accessibility
You can access your data from anywhere in the world.
Ideal for remote teams.
E) Automatic Updates
Providers handle software & hardware updates.
F) High Security
Cloud providers use:
- Encryption
- Firewalls
- Identity management
- AI-based threat detection
6. Real-World Use Cases of Cloud Computing
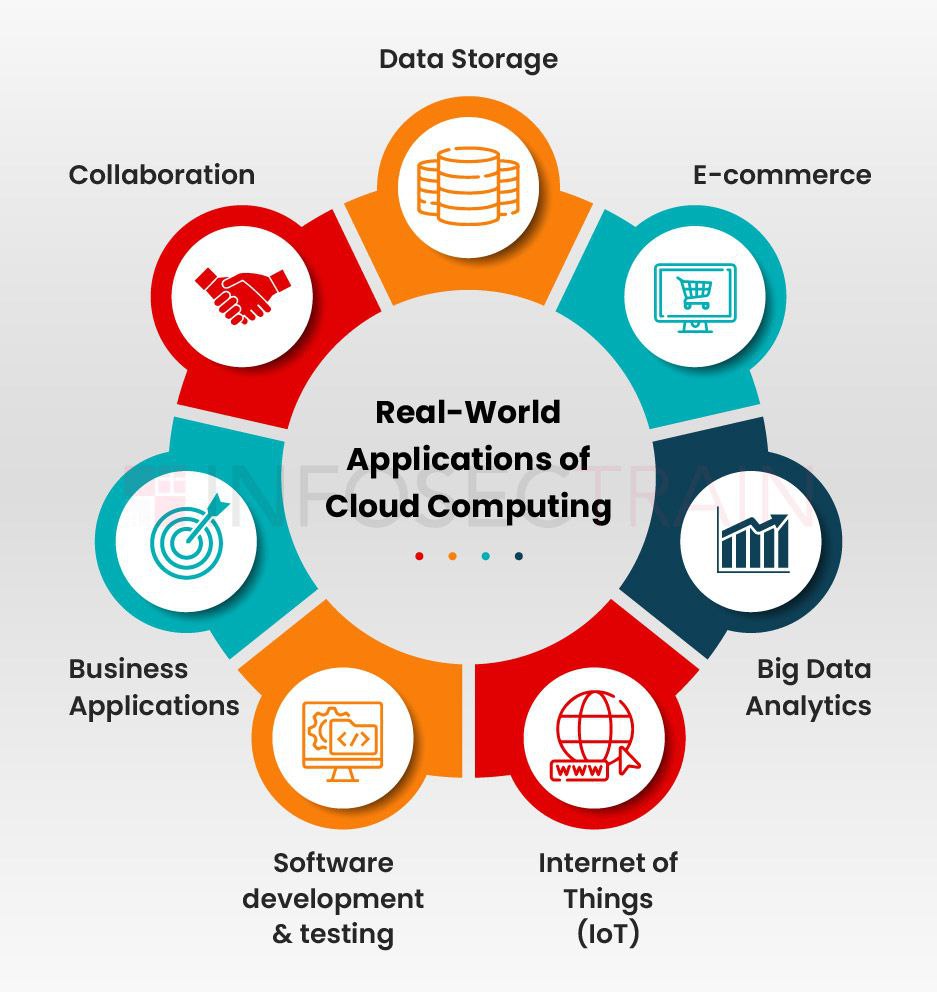

1. Streaming Services
Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify use the cloud to deliver movies and music to billions of users.
2. Social Media Platforms
Facebook, Instagram, TikTok store massive user data using cloud storage systems.
3. E-Commerce
Amazon and Shopify use cloud for:
- Order management
- AI recommendations
- Global delivery systems
4. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI models require large computing power.
Cloud providers offer:
- GPUs
- AI training environments
- Big data tools
5. Online Gaming
Cloud gaming services like NVIDIA GeForce Now run games on the cloud instead of your PC.
6. Banking & Finance
Banks use cloud for:
- Fraud detection
- Transaction processing
- Online banking systems
7. Healthcare
Cloud stores patient data securely and enables telemedicine.
8. Startups & SaaS Companies
Most startups launch using cloud infrastructure because it’s cheap and scalable.
7. Challenges of Cloud Computing
Even though cloud is powerful, it has some challenges.
A) Downtime
If the cloud provider goes down, your website may stop working.
B) Security Concerns
Cloud must be configured properly to avoid attacks.
C) Vendor Lock-In
Switching providers can be difficult.
D) Cost Management
Poor configuration can lead to high bills.
8. Future of Cloud Computing (2025 & Beyond)
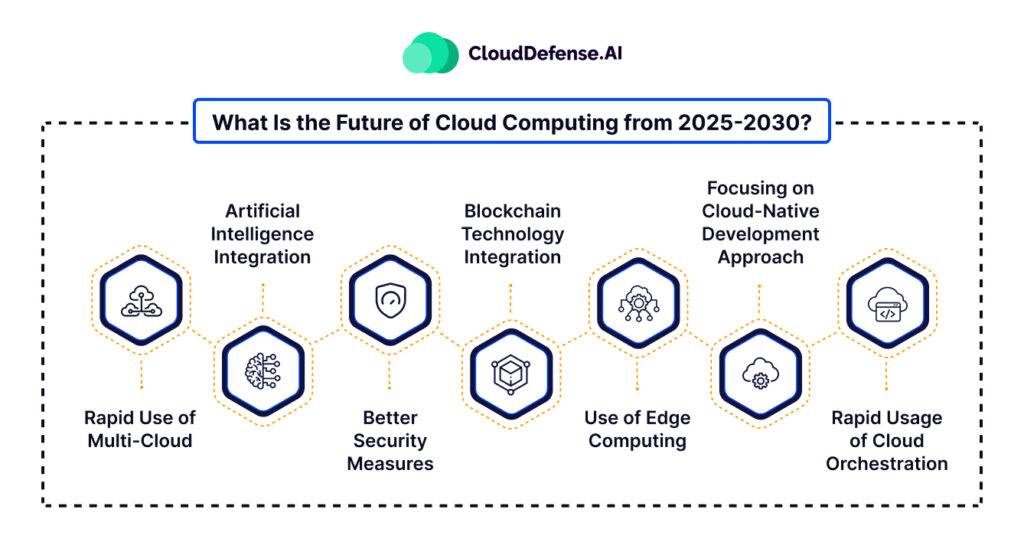

A) AI-Integrated Cloud
AI will automate cloud operations.
B) Serverless Computing
Run code without managing servers.
C) Quantum Cloud
Future computers will run quantum workloads.
D) Edge Computing
Faster processing by bringing cloud closer to users.
E) Green Cloud Technologies
Data centers will become energy-efficient.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the foundation of modern technology. It powers our apps, websites, devices, businesses, and global digital economy. Whether you’re a beginner or a professional, understanding cloud computing is essential in 2025.
From lower costs to better performance, the cloud helps businesses innovate faster and compete globally. And with the rise of AI, edge computing, and automation, the future of the cloud is brighter than ever.





Leave a Reply